Balancing Innovation and Impact: Can AI Truly Drive Sustainable Change?
As Artificial Intelligence becomes increasingly popular, how can we ensure its sustainability?
While AI (Artificial Intelligence) has the potential to aid in addressing and managing various environmental challenges, it also poses its own set of sustainability concerns. These concerns are largely concentrated around the proliferation of data centers, which house AI servers. These centers consume significant amounts of natural resources and electricity, prompting alarm among various environmental organizations, including the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)1. Nevertheless, there are several strategies to mitigate the environmental impact of AI and leverage its capabilities to effect positive change.
The Positive Impacts of AI
There is little doubt that AI can play a powerful role in addressing climate change. Already, companies such as Google have used it to create innovative sustainability solutions. In 2021, Google launched a feature in Google Maps that allows users to search for the most environmentally friendly route to their destination. This feature optimizes routes by considering factors such as elevation, traffic conditions, and maintaining a constant speed, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions2.
AI has also been used to promote sustainability in many other ways. It can monitor environmentally damaging practices, such as sand dredging3, and even map methane emissions4. Climate Change AI, an organization committed to fighting climate change through machine learning, has utilized AI to assess flood damage in Fiji, enabling timely and effective responses from government agencies5.
Utilizing AI for writing and illustration can also significantly reduce carbon emissions in the creative process. One study found that AI systems emit between 130 and 1,500 times less CO2e per page of text generated when compared to human writers6. This substantial reduction is largely due to the efficiency of AI, which produces content in much less time than it takes a human. This is one of the reasons why Brightest has implemented an AI tool to write answers to sustainability reports, reducing CO2 emissions.
Environmental Damage from AI
Artificial Intelligence holds significant promise for enhancing our approaches to sustainability; however, it also presents notable environmental challenges that require careful consideration. AI servers are housed in data centers, which are known for their substantial energy and water consumption. The cooling processes utilized in these facilities result in high water usage, and projections indicate that by 2027, global AI demand for water could reach between 4.2 and 6.6 billion cubic meters annually. As freshwater scarcity increases, the thirsty nature of AI presents an urgent environmental and ethical dilemma7.
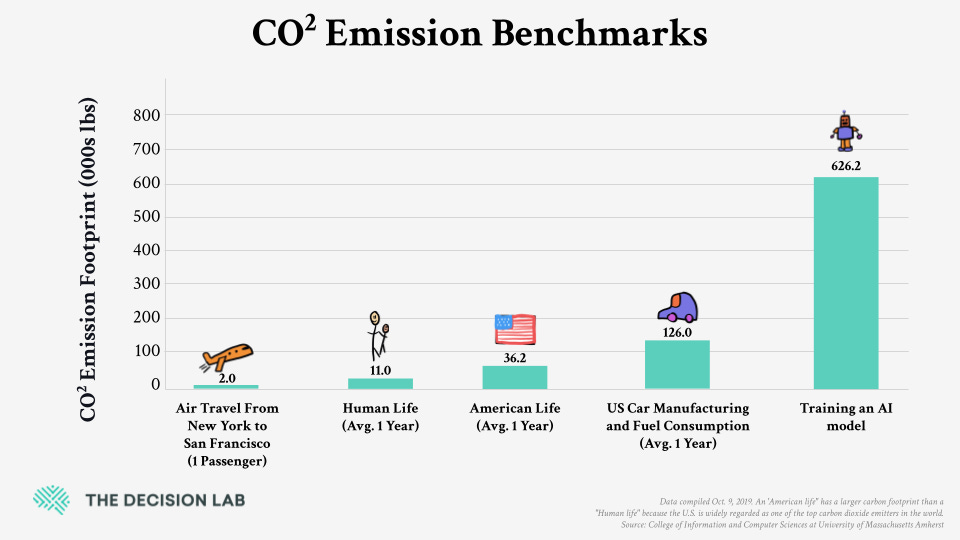
Another significant environmental concern associated with Artificial Intelligence is its carbon footprint. The operation of AI servers is energy-intensive, particularly in regions where electricity is generated from nonrenewable resources, resulting in a substantial carbon footprint8. Additionally, the training of AI models consumes considerable energy, further contributing to overall greenhouse gas emissions9.
3 Ways to Reduce the Impact of AI
So, how can we make Artificial Intelligence more sustainable? There are a few major steps we can take to reduce the environmental impact of AI.
Use Renewable Energy
Switching to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric energy, drastically reduces the carbon footprint of data centers thereby making AI more environmentally friendly and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Improve Efficiency
There are several ways that the efficiency of AI can be improved. First, more energy-efficient algorithms could reduce the energy consumption of running AI10. Companies like Schneider Electric are also working to reduce the energy consumption and water usage of data centers by utilizing IoT sensors.
Promote Circularity
The machinery that makes up AI systems is often made up of finite resources that are environmentally damaging to obtain. By extending the hardware lifespan through maintenance, making sure to recycle outdated equipment, and repurposing waste heat in data centers, we can significantly reduce the environmental impact of AI technology, promote sustainability, and enhance overall energy efficiency in the industry.
In Summation
In conclusion, while Artificial Intelligence offers remarkable potential for addressing pressing environmental issues, it also poses significant sustainability challenges that must be addressed. The energy and water consumption associated with AI data centers, along with their considerable carbon footprint, emphasize the need for continued innovation. By leveraging strategies such as transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing operational efficiency, and promoting a circular economy, we can mitigate the negative environmental impacts of AI. As we continue to integrate AI into various sectors, prioritizing sustainable practices will be crucial for ensuring that this technology contributes positively to our environmental future rather than exacerbating existing challenges. Through collective action and innovation, we can harness the power of AI to foster a more sustainable world.
This Week in Sustainability is a weekly email from Brightest (and friends) about sustainability and climate strategy. If you’ve enjoyed this piece, please consider forwarding it to a friend or teammate. If you’re reading it for the first time, we hope you enjoyed it enough to consider subscribing. If we can be helpful to you or your organization’s sustainability journey, please be in touch.
https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/ai-has-environmental-problem-heres-what-world-can-do-about
https://mapsplatform.google.com/resources/blog/navigate-more-sustainably-and-optimize-fuel-savings-eco-friendly-routing/
https://unepgrid.ch/en/marinesandwatch
https://www.unep.org/topics/energy/methane/international-methane-emissions-observatory
https://www.climatechange.ai/blog/2022-09-06-grants-fiji-flood
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-54271-x#:~:text=This%20figure%20compares%20the%20CO2e,to%20support%20humans%20making%20images.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.03271
https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/12/05/1084417/ais-carbon-footprint-is-bigger-than-you-think/
https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/11/14/1063192/were-getting-a-better-idea-of-ais-true-carbon-footprint?truid=&utm_source=the_algorithm&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=the_algorithm.unpaid.engagement&utm_content=12-04-2023
https://www.manufacturingtodayindia.com/the-energy-intensity-of-ai-the-environmental-impacts